
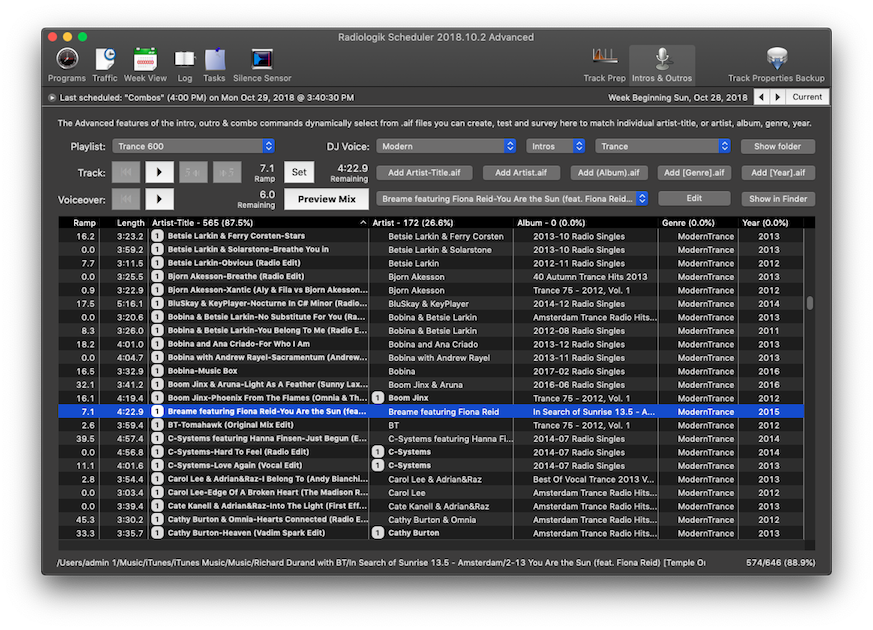
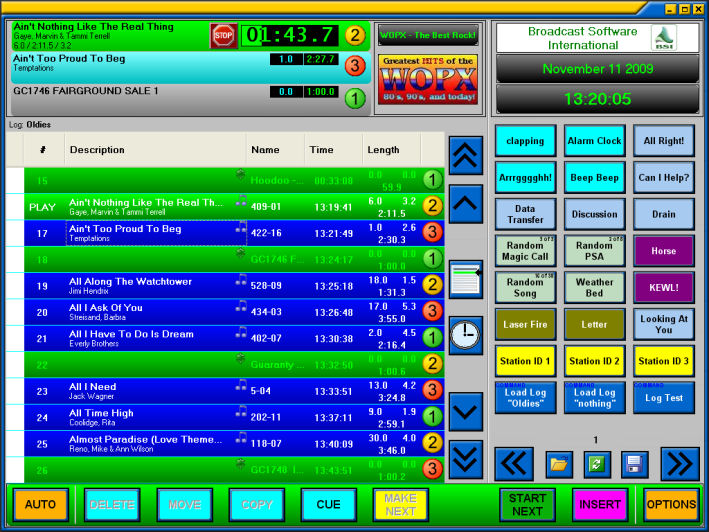
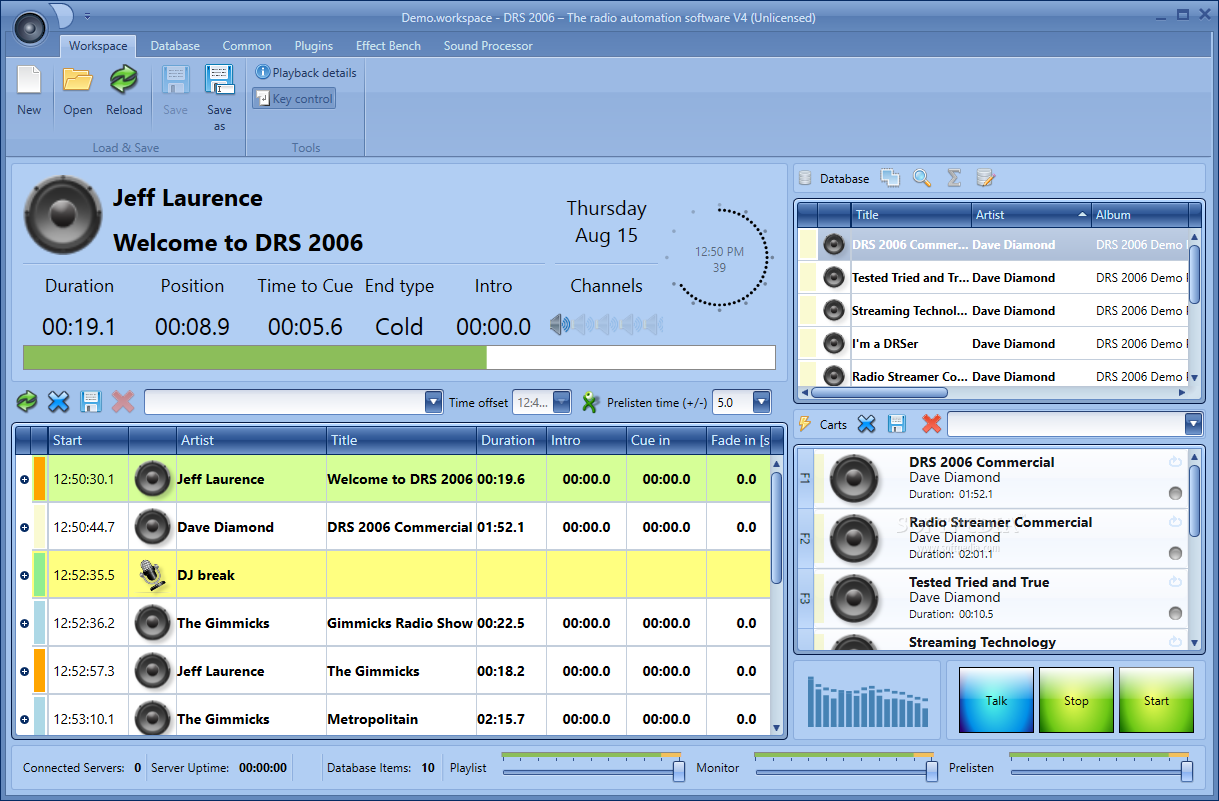
Built using the Syntiant Core 2™ programmable deep learning architecture, NDP200 is designed to natively run a variety of deep neural networks (DNN), such as CNN, RNN, and fully connected networks, and it performs vision processing with highly accurate inference at under 1mW. The NDP200 applies neural processing to run multiple applications simultaneously with minimal battery power consumption. The Syntiant NDP200 is a special-purpose neural decision processor for deep learning and is ideal for always-on applications in battery-powered devices. Based on this technology, we also launched a commercial company that helps the industry solve its Edge AI problems. Our research is highlighted by full-stack optimizations, including the neural network topology, inference library, and hardware architecture, which allows a larger design space to unearth the underlying principles. This enables us to deploy real-world AI applications on tiny microcontroller units (MCUs), despite the limited memory size and compute power. The fundamental cause of this problem is the mismatch between AI models and hardware, and we are solving it from the root by improving the efficiency of a neural network through model compression, neural architecture rebalances, and new design primitives. Today’s AI is too big, as modern deep learning requires a massive amount of computational resources, carbon footprint, and engineering efforts. This makes TinyML extremely difficult because of the limited hardware resource, the power budget, and the deploying challenges.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
